Role of Lean Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- Çağkan Ekici
- Apr 27, 2022
- 3 min read
Updated: Nov 15, 2023

In recent years, Six Sigma has become one of the most influential quality management methodologies in the world. Six Sigma, which has its origin in manufacturing, is also deployed in the banking sector, healthcare, and software development. A new iteration of the methodology that adds lean management principles to Six Sigma; is Lean Six Sigma.
Lean manufacturing is used to minimize waste and save costs. Lean manufacturing also strives to maintain/increase productivity. On the other hand, Six Sigma principles aim to reduce costs, improve processes and maximize production value. Lean Six Sigma, the popular new approach to process improvement, combines the best by reducing variation and waste and focusing on the customer's needs.
Fundamentally, Lean Six Sigma is a process improvement approach to eliminate inefficiencies and improve industrial processes by identifying the defect root causes analysis.
Let's find out more about these two approaches individually.
A Brief History of Lean and Six Sigma
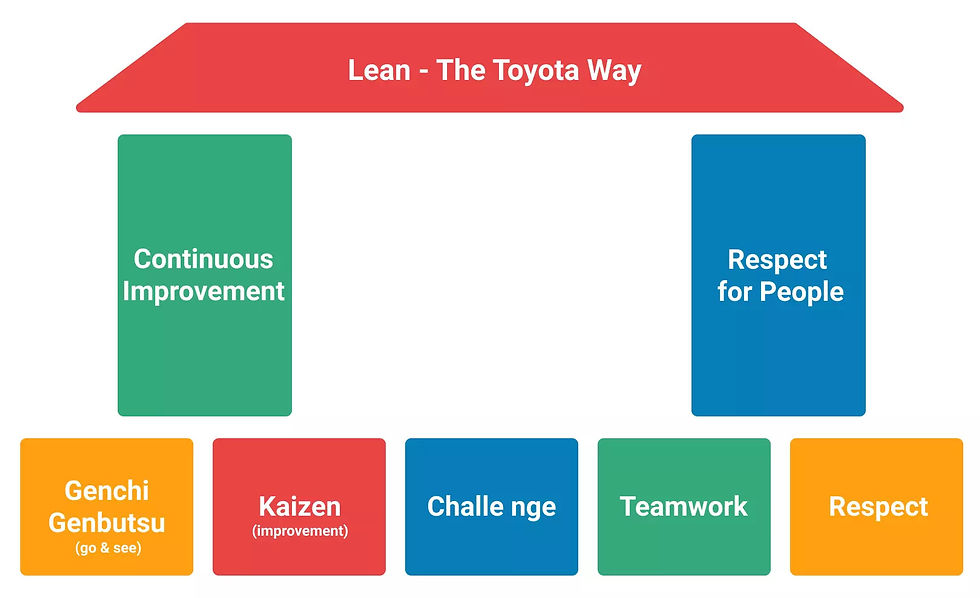
Lean manufacturing is a systematic method that wastes reduction in processes. Lean management methodology originated in Japan in the late 1940s as the Toyota Production System, which was established by Toyota in the late 1940s to reduce all non value adding activities from the process.
Lean emphasizes employee engagement in the transformation of the processes they carry out. One of the key steps of lean is to draw a Value Stream Map (VSM) of the series of activities that bring the product or service from the starting point to the customer.
Six Sigma methodology for project management was developed in 1986 by Motorola as a set of tools and techniques to improve the manufacturing processes. The concept was used by Jack Welch as the main concept of the business strategy of General Electric in 1995 and now it is used in various industrial sectors. And now, most the Fortune 500 companies adopt the Six Sigma concept for their operations.
The resulting combination of Lean and Six Sigma emerged in the beginning of 2000s. The Lean methodology highlights the sources of waste and the Six Sigma concept helps precisely measure performance, therefore they enable iterative improvement.

Lean Six Sigma highlights driving operational improvements using a framework with five phases: define, measure, analyze, improve, and control (DMAIC). All tools of Lean and Six Sigma can be classified in these stages and all improvement processes are subject to this overarching framework. Moreover, Lean Six Sigma training uses the same judo-inspired belt skill-level certification (White Belt, Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt and Master Black Belt) used in Six Sigma.
Benefits of Using Lean Six Sigma
Six Sigma began in the manufacturing industry, but it soon became obvious that the Six Sigma method could add value beyond the production floor. With the addition of Lean methodologies, Lean Six Sigma became a comprehensive methodology not only for manufacturing, but also for energy, transportation, and electronics sectors as well.
Sermin Vanderbilt stressed that, Founder of Lean and Six Sigma World Conference and President of the American Quality Institute, “If companies are successful, chances are they are implementing Lean, more than their competitors.”
Improved processes: By identifying and eliminating all waste and inefficiencies from the processes, companies facilitate maintenance and control through improved processes.
Increased revenues/Decreased cost: Creating advanced work where process steps are simple and all waste is eliminated will accelerate operations and improve quality. This will create a potential revenue increase. Also, by identifying and analyzing defects’ root causes, companies are able to decrease potential additional costs.
Analytical thinking: Operators can be more analytical as they transform complex problems into more manageable tasks through the Lean Six Sigma methodology. This helps identify root causes, so operators are able to create a clear understanding of where it needs to be improved.
Effectiveness: Through identifying the root causes, analyzing performance, and applying a hands-on solution, operators become more efficient in their roles. More specifically, their readiness to act on any process or problem creates a shared problem solving attitude that is a condition for continuous improvement.
Wrapping Up
You have a deeper understanding of what Lean Six Sigma methodology is and the benefits it brings, now it is time to start the change in your production line!
In order to achieve success with implementing Lean Six Sigma, it is essential that you understand and grasp the first steps involved in the process. As Khenda, we desire to provide companies with a solid foundation to guarantee effective process improvement initiatives.
There’s never been a better time to adopt a process improvement methodology. Try Khenda for free, today!
References:



